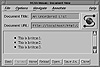
FIG. 32.5 An unordered list displayed in Mosaic.
| Previous | Table of Contents | Next |
Table 32.1 provides a quick listing of some of the most common HTML tags for text formatting.
| Tag | Action |
|---|---|
| <B>…</B> | Makes text bold. |
| <BLOCKQUOTE>…</BLOCKQUOTE> | Formats text with left and right indents. |
| <FONT>…</FONT> | Controls various aspects of text with attributes—for example, text color (COLOR=rgb_value) and size (SIZE=number). |
| <I>…</I> | Makes text italic. |
| <PRE>…</PRE> | Leaves text formatting exactly as it appears. |
| <STRIKE>…</STRIKE> | Formats text as |
| <U>…</U> | Underlines text. |
| <EM>…</EM> | Logical style; emphasizes text (typically displayed as italic). |
| <KBD>…</KBD> | Logical style; shows text as a keyboard style (usually displayed in a monospaced font). |
| <STRONG>…</STRONG> | Logical style; emphasizes text (typically displayed as bold). |
Miscellaneous Text
Two formatting tags that don’t fit in with other tag categories are the <ADDRESS> and </ADDRESS> tags. These tags are used to mark addresses, signatures, and so on within a document. Typically, text with this format is placed at the end of a document, following a horizontal rule mark. The exact formatting of <ADDRESS> text is determined by the individual Web browser.
Sometimes you need to deliver information that’s logically grouped in some fashion. For example, you might have a list of graphic images to display, or you might want to show a numbered top 10 list. HTML provides several different ways to format and display lists of information. Using lists in HTML is a powerful way to deliver information, because the user’s Web browser formats all the text in the list in a consistent manner. All you have to do is decide how the information fits together.
Displaying Unordered Lists
An unordered list is text displayed separately with a bullet or other formatting character. Each text entry in an unordered list can be several lines long.
Two sets of tags are used to create an unordered list. The <UL> and </UL> tags define the beginning and end of the list, and the <LI> tag is used to mark each list item. Listing 32.4 shows the HTML source for a simple unordered list. Figure 32.5 shows how Mosaic displays this list.
Listing 32.4 An Unordered List
<HTML> <HEAD> <TITLE>An Unordered List</TITLE> </HEAD> <BODY> <LI>This is list item 1. <LI>This is list item 2. <LI>This is list item 3. </UL> </BODY> </HTML>

FIG. 32.5 An unordered list displayed in Mosaic.
Presenting Ordered Lists
An ordered list presents list information in numerical order. Each time a new list item is identified, the number of the list item is incremented. Ordered lists are defined by the <OL> and </OL> tags, and the same <LI> tag used in unordered lists is also used in ordered lists to mark each list item.
Listing 32.5 shows the HTML source for a simple ordered list. Figure 32.6 shows how this list is displayed in Mosaic.
Listing 32.5 An Ordered List
<HTML> <HEAD> <TITLE>An Ordered List</TITLE> </HEAD> <BODY> <OL> <LI>This is list item 1. <LI>This is list item 2. <LI>This is list item 3. </OL> </BODY> </HTML>
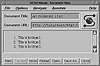
FIG. 32.6 An unordered list displayed in Mosaic.
Using Definition Lists
Think of how a glossary in a book looks: You typically have each word or term offset by itself and then a paragraph giving its definition. HTML definition (or glossary) lists provide a way to do this with Web pages. A definition list consists of a term—this can be one word or a series of words—followed by a definition. The definition is usually explanatory text.
Although definition lists are particularly useful for glossaries, you can use them to present any kind of information where you need a title and an explanation. One common use is to make the glossary term a hypertext link to another document and make the definition a description of the linked document. (Creating hypertext links is discussed later in this chapter, so keep this application of a definition list in mind.)
Definition lists require the <DL> and </DL> tags to mark the start and end of the list. Rather than use a simple list item tag, definition lists use dual tags: <DT> to mark the glossary item and <DD> to mark the definition. Listing 32.6 shows the HTML source for a simple definition list. Figure 32.7 shows how this list is displayed in Mosaic.
Listing 32.6 A Simple Definition List
<HTML> <HEAD> <TITLE>A Simple Glossary List</TITLE> </HEAD> <BODY> <DL> <DT>Item 1 <DD>This is the definition field for list item 1. <DT>Item 2 <DD>This is the definition field for list item 2. <DT>Item 3 <DD>This is the definition field for list item 3. </DL> </BODY> </HTML>
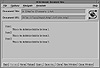
FIG. 32.7 A simple definition list displayed in Mosaic.
| Previous | Table of Contents | Next |