| Previous | Table of Contents | Next |
sxpm......Show X Pixmap

sxpm option(s) filename
PURPOSE
The sxpm displays an X pixmap (graphics) file and can convert files formatted with the XPM 1 or XPM 2 format to the newer XPM 3 format.
OPTIONS
| -closecolors | Uses “close colors” before reverting to other visuals. |
| -color | Displays the colors specified for a color visual. |
| -cp colorname pixelvalue | Overrides colorname color to pixelvalue. |
| -d display | Specifies the display to connect to. |
| -g geom | Sets the window geometry (the default is the pixmap size). |
| -grey | Displays the colors specified for a greyscale visual. |
| -grey4 | Displays the colors specified for a 4-color greyscale visual. |
| -hints | Sets ResizeInc hints for the window. |
| -icon filename | Creates an icon from pixmap created from the file filename. |
| -mono | Displays a monochrome visual. |
| -nod | Does not display the pixmap in a window; use this option when converting between formats. |
| -nom | Ignores a clipmask. |
| -o filename | Write to filename. |
| -pcmap | Uses a private colormap. |
| -plaid | Shows a plaid pixmap stored as data. |
| -sc symbol colorname | Overrides symbol color to colorname. |
| -sp symbol pixelvalue | Overrides symbol color to pixelvalue. |
| -rgb filename | Searches the RGB database in filename and writes them out instead of the default RGB values. |
| -v | Prints extensions in verbose mode. |
systat......System Statistics
systat option(s) hostname
PURPOSE
The systat command checks a specified hostname for system information via the hostname’s own systat service. If the systat service isn’t available, daytime or netstat information is queried.
OPTIONS
| -n | Query the netstat service. |
| -p port | Specify a port on the host. |
| -s | Query the systat service (the default setting). |
| -t | Query the daytime service. |
| --netstat | Query the netstat service. |
| --port port | Specify a port on the host. |
| --systat | Query the systat service (the default setting). |
| --time | Query the daytime service. |
sz......Send Zmodem
sz option(s) command
PURPOSE
The sz command sends a file to another system using the Zmodem protocol. There’s a long list of options to this command; see the online-manual page for more information.
tee......Send Information to Two Files
tee option filenames
PURPOSE
The tee command sends the output of a command to two separate files. If the files already exist, the tee command will overwrite the contents of the files.
OPTION
| -a | Appends routed information to filenames, but does not overwrite existing files. |
EXAMPLE
$ tee output.kr output.pv
tload......Total Systems Load
tload option(s)
PURPOSE
The tload command lists the system load in a graph.
OPTIONS
| -d delay | Sets the delay between graph updates in seconds. |
| -s scale | Specifies a vertical scale. |
RELATED COMMANDS
top......Top Processes
top option(s)
PURPOSE
The top command lists the top processes on the system—that is, those processes that are using the most CPU time.
OPTIONS
| d | Specifies the delay between screen updates. |
| q | Refreshes without any delay. |
| S | Lists CPU time of dead children as well. |
| s | Runs in secure mode. |
| i | Ignores zombie or idle processes. |
EXAMPLE
$ top
RELATED COMMANDS
true......Returns True
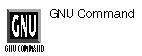
true
PURPOSE
The true command does nothing except return an exit status of 0, which means success. This is useful in shell scripts.
ul......Underline
ul option(s) terminals
PURPOSE
The ul command changes all underscored text to underlined text. This is an issue for terminal users hooked to a Linux system, not to most Linux users.
OPTIONS
| -i | Uses a separate line containing appropriate dashes for underlining. |
| -t terminal | Specifies a new terminal type. |
unshar......Unpack Shar File
unshar option(s) filename
PURPOSE
The unshar command unpacks a shar file.
OPTIONS
| -c | Overwrites existing files. |
| -d directory | Changes the directory to directory before unpacking files. |
RELATED COMMAND
uptime......System Information
uptime
PURPOSE
The uptime command tells how long the system has been running, how many users are currently logged on, and the system-load averages for the past 1, 5, and 15 minutes.
RELATED COMMANDS
users......User Information
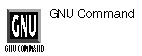
users filename
PURPOSE
The users command lists information about the users currently logged in the Linux system, based on information found in the /etc/utmp file. If you want information from another system file, you must specify it on the command line.
RELATED COMMANDS
| Previous | Table of Contents | Next |