| Previous | Table of Contents | Next |
tac......Reverse Cat
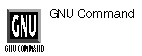
tac option(s) filename
PURPOSE
The tac command (opposite of cat) is used to display files in reverse order; that is, the ending line of a file is displayed first, followed by the second-to-the-last line, and so on.
OPTIONS
| -b | Attaches the separator to the beginning of the record that precedes it. |
| -r | Sets the separator to a regular expression. |
| -s string | Sets string as the record separator. |
RELATED COMMAND
tail......Print End of File
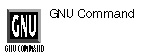
tail option(s) filename
PURPOSE
The tail command prints the last 10 lines of filename to the screen. You can display more or less of the file using options. The command is the opposite of the head command, used to display the first 10 lines of a file.
OPTIONS
| -c num | Displays num number of bytes. |
| -f | Loops forever trying to read more characters at the end of the file, on the assumption that the file is growing. |
| -l num | Displays num number of lines. |
| -q | Does not print filename headers. |
| -v | Prints filename headers. |
RELATED COMMAND
tr......Translate Characters
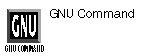
tr option(s) [string1 [string2]]
PURPOSE
The tr command translates or deletes characters, replacing string1 with string2.
troff......Format Documents
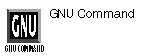
troff option(s) filename
PURPOSE
The troff command is a text formatter, part of the groff family of formatters. You usually don’t use it on your own. Rather, it is invoked by the groff command on its own. Check the groff command for more information.
RELATED COMMANDS
Unexpand......Unexpand File
unexpand option(s) filename
PURPOSE
The unexpand command converts spaces to tabs in a textfile.
OPTIONS
| -a | Converts all strings of two or more spaces or tabs, not just initial ones, to tabs. |
| -t tab1 | Set the tabs tab1 spaces apart, instead of the default 8. |
uniq......Create Unique Files
uniq option(s) filename1 filename2
PURPOSE
The uniq command strips duplicate lines from a specified file (filename1) and then sends them either to another file (filename2) or to standard output is no other file is named.
OPTIONS
| -c | Counts duplicate lines. |
| -d | Returns duplicate lines, but no unique lines. |
| -fn | Skips the first n fields of a line; fields are separated by spaces or tabs. |
| -sn | Skips the first n characters of a field; fields are separated by spaces or tabs. |
| -u | Returns unique lines, and duplicate lines are sent to the ether. |
| -w n | Compares the first n characters of a line. |
| -n | Skips the first n fields of a line; fields are separated by spaces or tabs. |
| +n | Skips the first n characters of a field; fields are separated by spaces or tabs. |
| --check-chars=n | Compares the first n characters of a line. |
| --skip-chars=n | Skips the first n characters of a field; fields are separated by spaces or tabs. |
| --skip-fields=n | Skips the first n fields of a line; fields are separated by spaces or tabs. |
RELATED COMMANDS
vi......Text Editor
vi option(s) filename
PURPOSE
The vi command is actually a shortcut to the elvis text editor. (Technically, the vi editor found on other UNIX systems is not the same vi as this one.) See elvis for more information.
vim......Vi Improved
vim option(s) filename
PURPOSE
The vim text editor is an vi-compatible text editor useful for editing text files. See the online-manual pages for a list of the available options.
wc......Word Count
wc option(s) filename
PURPOSE
The wc command counts the words in a text file; if no filename is specified, then standard input is counted. This is a handy command when combined with other text-processing commands within a pipeline.
OPTIONS
| -bytes | Prints the character count. |
| -c | Prints the character count. |
| --chars | Prints the character count. |
| -l | Prints the number of lines in the file. |
| --lines | Prints the number of lines in the file. |
| -w | Prints the number of words in the file; this is the default. |
| --words | Prints the number of words in the file; this is the default. |
EXAMPLE
$ wc textfile 324
xedit......X Editor

xedit filename(s)
PURPOSE
The xedit command launches a simple text editor running under the X Window System.
zcmp......Compare Compressed Files
zcmp option(s) file(s)
PURPOSE
The zcmp command uncompresses a gzip compressed file and calls on cmp. The options associated with this command are actually cmp options, which are passed along to cmp along with the compressed file.
RELATED COMMANDS
| Previous | Table of Contents | Next |