


- A -
Java Language Reference
This appendix contains a summary or quick reference for the Java language, as described in this book.
 Technical Note: This is neither a grammar, nor is it a technical overview of the language itself. It's a quick reference to be used after you already know the basics of how the language works. If you need
a technical description of the language, your best bet is to visit the Java Web Site (http://java.sun.com) and download the actual specification, which includes a full description of the Java language.
Technical Note: This is neither a grammar, nor is it a technical overview of the language itself. It's a quick reference to be used after you already know the basics of how the language works. If you need
a technical description of the language, your best bet is to visit the Java Web Site (http://java.sun.com) and download the actual specification, which includes a full description of the Java language.
Language keywords and symbols are shown in a monospace font. Arguments and other parts to be substituted are in italic monospace.
Optional parts are indicated by brackets (except in the array syntax section). If there are several options that are mutually exclusive, they are shown separated by pipes (|) like this:
[ public | private | protected ] type varname
Reserved Words
The following words are reserved for use by the Java language itself (some of them are reserved but not currently used). You cannot use these terms to refer to classes, methods, or variable names:
|
abstract
|
double
|
int
|
static
|
|
boolean
|
else
|
interface
|
super
|
|
break
|
extends
|
long
|
switch
|
|
byte
|
final
|
native
|
synchronized
|
|
case
|
finally
|
new
|
this
|
|
catch
|
float
|
null
|
throw
|
|
char
|
for
|
package
|
throws
|
|
class
|
goto
|
private
|
transient
|
|
const
|
if
|
protected
|
try
|
|
continue
|
implements
|
public
|
void
|
|
default
|
import
|
return
|
volatile
|
|
do
|
instanceof
|
short
|
while
|
Comments
|
/*
|
this is a multiline comment */
|
|
//
|
this is a single-line comment
|
|
/**
|
Java documentation comment */
|
Literals
|
number
|
Type int (for example, 8)
|
|
number[l | L]
|
Type long (for example, 4527543L)
|
|
0xhex
|
Hex integer (for example, 0x3F8)
|
|
0Xhex
|
Hex integer (for example, 0X3F8)
|
|
0octal
|
Octal integer (for example, 034)
|
|
[ number ].number
|
Type double (for example, 2483.875)
|
|
number[ f | F]
|
Type float (for example, 435f)
|
|
number[ d | D]
|
Type double (for example, 435d)
|
|
[ + | - ] number
|
Signed (for example, -345.67)
|
|
numberenumber
|
Exponent (for example, 234.95e6)
|
|
numberEnumber
|
Exponent (for example, 234.95E6)
|
|
'character'
|
Single character
|
|
"characters"
|
String
|
|
""
|
Empty string
|
|
\b
|
Backspace
|
|
\t
|
Tab
|
|
\n
|
Line feed
|
|
\f
|
Form feed
|
|
\r
|
Carriage return
|
|
\"
|
Double quote
|
|
\'
|
Single quote
|
|
\\
|
Backslash
|
|
\uNNNN
|
Unicode escape (NNNN is hex)
|
|
true
|
Boolean
|
|
false
|
Boolean
|
Variable Declaration
|
[ byte | short | int | long ] varname
|
Integers
|
|
[ float | double ] varname
|
Floats
|
|
char varname;
|
Characters
|
|
boolean varname
|
Boolean
|
|
classname varname;
|
Class types
|
|
interfacename varname;
|
Interface types
|
|
type varname1[, varnameN];
|
Multiple variables
|
The following options are available only for class and instance variables. Any of these options can be used with a variable declaration:
|
[ static ] variableDeclaration
|
Class variable
|
|
[ final ] variableDeclaration
|
Constants
|
|
[ public | private | protected ] variableDeclaration
|
Access control
|
|
[ volatile ] varname
|
Modified asynchronously
|
|
[ transient ] varname
|
Not persistent
|
Variable Assignment
|
variable = value
|
Assignment
|
|
variable++
|
Postfix Increment
|
|
++variable
|
Prefix Increment
|
|
variable--
|
Postfix Decrement
|
|
--variable
|
Prefix Decrement
|
|
variable += value
|
Add and assign
|
|
variable -= value
|
Subtract and assign
|
|
variable *= value
|
Multiply and assign
|
|
variable ÷= value
|
Divide and assign
|
|
variable %= value
|
Modulus and assign
|
|
variable &= value
|
AND and assign
|
|
variable |= value
|
OR and assign
|
|
variable ^= value
|
XOR and assign
|
|
variable <<= value
|
Left-shift and assign
|
|
variable >>= value
|
Right-shift and assign
|
|
variable <<<= value
|
Zero-fill right-shift and assign
|
Operators
|
arg + arg
|
Addition
|
|
arg - arg
|
Subtraction
|
|
arg * arg
|
Multiplication
|
|
arg ÷ arg
|
Division
|
|
arg % arg
|
Modulus
|
|
arg < arg
|
Less than
|
|
arg > arg
|
Greater than
|
|
arg <= arg
|
Less than or equal to
|
|
arg => arg
|
Greater than or equal to
|
|
arg == arg
|
Equal
|
arg 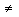 arg arg
|
Not equal
|
|
arg && arg
|
Logical AND
|
|
arg || arg
|
Logical OR
|
|
! arg
|
Logical NOT
|
|
arg & arg
|
AND
|
|
arg | arg
|
OR
|
|
arg ^ arg
|
XOR
|
|
arg << arg
|
Left-shift
|
|
arg >> arg
|
Right-shift
|
|
arg >>> arg
|
Zero-fill right-shift
|
|
~ arg
|
Complement
|
|
(type)thing
|
Casting
|
|
arg instanceof class
|
Instance of
|
|
test ? trueOp : falseOp
|
Ternary (if) operator
|
Objects
|
new class();
|
Create new instance
|
|
new class(arg1[,argN])
|
New instance with parameters
|
|
object.variable
|
Instance variable
|
|
object.classvar
|
Class variable
|
|
Class.classvar
|
Class variable
|
|
object.method()
|
Instance method (no args)
|
|
object.method(arg1[,argN])
|
Instance method
|
|
object.classmethod()
|
Class method (no args)
|
|
object.classmethod(arg1[,argN])
|
Class method
|
|
Class.classmethod()
|
Class method (no args)
|
|
Class.classmethod(arg1[,argN])
|
Class method
|
Arrays
 Note: The brackets in this section are parts of the array creation or access statements. They do not denote optional parts as they do in other parts of this appendix.
Note: The brackets in this section are parts of the array creation or access statements. They do not denote optional parts as they do in other parts of this appendix.
|
type varname[]
|
Array variable
|
|
type[] varname
|
Array variable
|
|
new type[numElements]
|
New array object
|
|
array[index]
|
Element access
|
|
array.length
|
Length of array
|
Loops and Conditionals
|
if ( test ) block
|
Conditional
|
|
|
|
|
|
if ( test ) block
|
|
|
|
else block
|
Conditional with
|
else
|
|
|
|
|
switch ( test ) {
|
switch (only with
|
integer
|
|
case value : block
|
or char types)
|
|
|
case value : block
|
|
|
|
...
|
|
|
|
default : block
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
for (initializer, test, change ) block
|
for loop
|
|
|
|
|
|
while ( test ) block
|
while loop
|
|
|
|
|
|
do block
|
do loop
|
|
|
while ( test )
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
break [ label ]
|
break from loop or
|
|
|
switch
|
|
|
|
|
|
continue [ label ]
|
continue loops
|
|
|
|
|
|
label:
|
Labeled loops
|
|
Class Definitions
The basic class definition looks like this:
|
class classname block
|
Simple Class definition
|
Any of the following optional modifiers can be added to the class definition:
|
[ final ] class classname block
|
No subclassed
|
|
[ abstract ] class classname block
|
Cannot be instantiated
|
|
[ public ] class classname block
|
Accessible outside package
|
|
class classname [ extends Superclass ] block
|
Define superclass
|
|
class classname [ implements interfaces ] block
|
Implement one or more interfaces
|
Method and Constructor Definitions
The basic method looks like this, where returnType is a type name, a class name, or void.
|
returnType methodName() block
|
Basic method
|
|
returnType methodName(parameter1[, parameterN]) block
|
Method with parameters
|
Method variations can include any of the following optional keywords:
|
[ abstract ] returnType methodName() block
|
Abstract method
|
|
[ static ] returnType methodName() block
|
Class method
|
|
[ native ] returnType methodName() block
|
Native method
|
|
[ final ] returnType methodName() block
|
final method
|
|
[ synchronized ] returnType methodName() block
|
Thread lock before executing
|
|
[ public | private | protected ] returnType methodName()
|
Block access control
|
Constructors look like the following:
|
classname() block
|
Basic constructor
|
|
classname(parameter1[, parameterN]) block
|
Constructor with parameters
|
|
[ public | private | protected] classname()block
|
Access control
|
In the method/constructor body you can use these references and methods:
|
this
|
Refers to current object
|
|
super
|
Refers to superclass
|
|
super.methodName()
|
Call a superclass' method
|
|
this(...)
|
Calls class' constructor
|
|
super(...)
|
Calls superclass' constructor
|
|
return [ value ]
|
Returns a value
|
Packages, Interfaces, and Importing
|
import package.className
|
Imports specific class name
|
|
import package.*
|
Imports all public classes in package
|
|
package packagename
|
Classes in this file belong to this package
|
|
interface interfaceName [ extends anotherInterface ] block
|
|
|
[ public ] interface interfaceName block
|
|
|
[ abstract ] interface interfaceName block
|
|
Exceptions and Guarding
|
synchronized ( object ) block
|
Waits for lock on object
|
|
|
|
try block
|
Guarded statements
|
|
catch ( exception ) block
|
Executed if exception is thrown
|
|
[ finally block ]
|
Cleanup code
|
|
|
|
try block
|
Same as previous example (can
|
|
[ catch ( exception ) block ]
|
use optional catch or finally,
|
|
finally block
|
but not both)
|




Technical Note: This is neither a grammar, nor is it a technical overview of the language itself. It's a quick reference to be used after you already know the basics of how the language works. If you need a technical description of the language, your best bet is to visit the Java Web Site (http://java.sun.com) and download the actual specification, which includes a full description of the Java language.
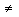 arg
arg
Note: The brackets in this section are parts of the array creation or access statements. They do not denote optional parts as they do in other parts of this appendix.